10 Essential Web Application Security Best Practices
by Yusra Saqib

Web application security is crucial for protecting sensitive data, maintaining user privacy, and defending against cyber attacks. It involves implementing security measures and best practices, to ensure that the application is resistant to attacks and unauthorized access.
“Making web applications safe is in the best interest of all organizations and the general economy. Providing a clearly defined set of web application security best practices will advance security professionals’ ability to anticipate and rapidly address potential threats to their enterprise.”
—Yuval Ben-Itzhak, CTO and Co-Founder KaVaDo
Web Application Security Best Practices
Web application security best practices refer to a set of recommended guidelines. These guidelines should be followed by organizations to ensure the security of web applications from potential threats. These practices are designed to minimize the risk of security breaches, unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber attacks.
10 Best Practices for Web Application Security
Implementing best practices for web application security is crucial. It helps to protect your application and its users from potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Here are some essential best security practices for web application to consider:
Secure Coding
Secure coding refers to the practice of writing code with a strong focus on security. It involves adopting secure coding practices and following established guidelines to develop software. This software is resistant to various types of cyber attacks.
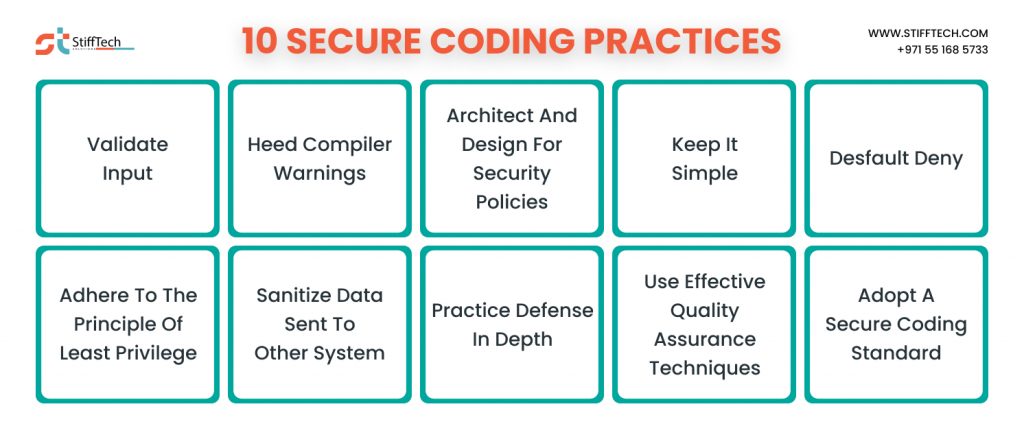
User Authentication and Authorization
The combination of user authentication and authorization ensures that users are properly identified, authenticated, and granted appropriate access rights within the web application.
Security best practices for user authentication and authorization include:
- Using strong and secure authentication methods, such as MFA, to prevent unauthorized access to user accounts.
- Enforcing the principle of least privilege to grant users only the minimum necessary permissions required for their roles.
- Regularly reviewing and updating user access rights as needed to align with changing roles and responsibilities.
- Implementing secure session management to control user sessions and prevent session-related attacks.
- Using proper encryption techniques to protect sensitive user credentials and data in transit and at rest.
Input Validation and Output Encoding
Input validation and output encoding work together to enhance web application security by ensuring that only valid and sanitized data is processed and presented to users. These practices are essential components of secure coding and should be applied consistently throughout the development process to mitigate security risks effectively.
Secure Communication
Secure communication is essential to protect sensitive data and ensure the privacy and integrity of information transmitted over networks. In the context of web applications, secure communication primarily focuses on safeguarding data exchanged.
Regular Updates and Patch Management
Keeping the software components of your web application up to date helps address security vulnerabilities.
To implement effective patch management and regular updates:
- Establish a process for monitoring and receiving notifications about software updates and security patches.
- Test updates and patches in a controlled environment before deploying them to the production environment.
- Have a well-documented change management process to ensure updates are applied systematically and consistently.
- Maintain a list of all software components and their versions to track update status easily.
- Set up automated systems to check for and apply updates when possible to ensure timely patching.
Security Testing
Security testing is a critical process in the development and deployment of web applications to identify and address potential security weaknesses. It involves a systematic evaluation of the application’s security controls. This is done to ensure that it can withstand various types of attacks.
Secure Configuration
Secure configuration ensures that the web application and its underlying infrastructure are set up with the best security practices to protect against potential threats. Regularly reviewing and updating configurations to align with security best practices is essential to maintain a strong security posture over time.
Least Privilege Principle
The least privilege principle refers to the practice of granting users and processes the minimum set of permissions required to perform their specific tasks or access certain resources.By applying the least privilege principle to web applications, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security incidents.
Access Control and Session Management
Proper access control prevents unauthorized users from gaining access to sensitive data or performing actions they are not allowed to execute. Session management ensures that users remain authenticated while interacting with the application and that their session-related data is properly handled.
Security Monitoring and Incident Response
Effective security monitoring and incident response practices help organizations identify and address security incidents promptly.
Java Web Application security best practices
Java web application security is of paramount importance to protect against potential vulnerabilities and attacks. Implementing best practices helps ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the application and its data.
Here are some essential Java web application security best practices:
Input Validation
Validate all user inputs on the server-side to prevent common vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and command injection. Use whitelisting and input encoding to ensure only safe and expected data is processed.
Protection against Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a popular issue and mostly utilized in JavaScript applications. Sanitize user-generated content before rendering it in web pages to prevent XSS attacks. Use security libraries or frameworks that offer built-in XSS protection.
Preventing Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
Include CSRF tokens in forms and requests to mitigate CSRF attacks. This prevents unauthorized actions from being executed on behalf of authenticated users.
ASP.NET web application security best practices
ASP.NET is a popular web application development framework developed by Microsoft, and it offers various security features and functionalities. But still its important to monitor the activities and apply best security practices.
Below are some of the best security practices:
Cross-Site Scripting
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) is a common web application security vulnerability. It allows attackers to inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users. It is a good practice to store authentic data in your database.
Cross-Site Request Forgery
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF), also known as XSRF, is a web application that allows attackers to perform unauthorized actions on behalf of authenticated users.
Web application security best practices OWASP
OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) is a non-profit organization focused on improving the security of web applications. They provide a comprehensive set of web application security best practices to help developers build secure applications.
Here are some key web application security best practices based on the OWASP Top Ten:
Injection Prevention
Use parameterized queries (prepared statements) to prevent SQL injection and validate/sanitize user inputs to prevent other types of injection vulnerabilities.
Authentication and Authorization
Implement strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), and use proper authorization controls to ensure users have access only to the resources they need.
Sensitive Data Exposure
If web applications don’t secure sensitive data like passwords and financial information. The attackers can get this data for malicious activities. Data exposure risk can be minimized by encrypting all the data.
Secure Configuration Management
Follow secure configuration practices for the web server, application server, and database to reduce the attack surface.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Mitigation
Sanitize user-generated content, encode output, and implement a Content Security Policy (CSP) to prevent XSS attacks.
Insecure Deserialization
Insecure deserialization is a web application security vulnerability that occurs when untrusted data is deserialized without proper validation. Deserialization is the process of converting data in a serialized format back into its original form, typically used for data exchange or storage.
Error Handling and Logging
Avoid revealing sensitive information in error messages and log security events properly for monitoring and incident response.
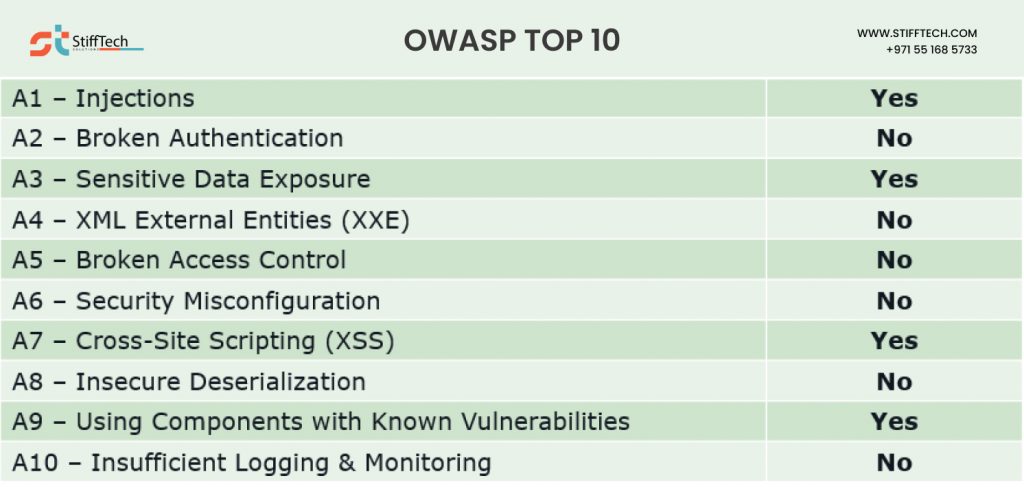
Using Components With Known Vulnerabilities
Using components with known vulnerabilities is a significant security risk for web applications and other software systems. These vulnerabilities are often publicly documented and known to malicious actors. To minimize the risk of running components with known vulnerabilities, developers should remove unused components from their projects.
Broken Access Control
Access control is the mechanism that determines what resources a user can access and what operations they can perform within the application. Access controls can be secured by ensuring that a web application uses authorization tokens* and sets tight controls on them.
XML External Entities (XEE)
XML External Entities (XEE) is a type of security vulnerability that occurs when an application processes XML input from untrusted sources without proper validation and sanitization. The best ways to prevent XEE attacks are to have web applications. They accept a less complex type of data, such as JSON**, and disable the use of external entities in an XML application.
Conclusion
Remember that web application security is an ongoing process, and it is essential to keep up with the latest security trends. By implementing these best practices, you can significantly enhance the security of your web application and protect it against potential threats.
Recommended Posts

Top 5 Outsourcing Software Development Companies
December 26, 2023

Digital Security-Safeguarding Data and Privacy in a Connected World
September 6, 2023

